Background
The study of bones can tell us information about a person who is no longer living. A skull provides information about the structure of a face, including key distances like those that we have used for face recognition. Forensic artists can use a skull to create a face image that is recognizable and useful in solving crimes. 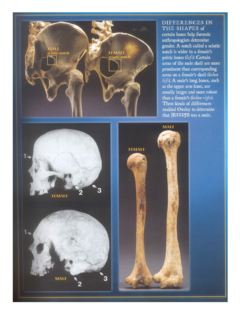
In addition, the gender and ethnicity of a person can be determined from the bones. A good illustration of bone differences is found in the book "Written in Bone - Buried Lives of Jamestown and Colonial Maryland," by Sally M. Walker. This book is on the junior high summer reading list for some schools.
You may have also heard about Carbon-14 dating. Organic molecules are made up of carbon, and other elements such as hydrogen and oxygen. All carbon atoms have 6 protons, but the number of neutrons varies. The number "14" indicates the number of protons and neutrons, so Carbon-14 has 8 neutrons, while Carbon-13 has 7 neutrons. The level of carbon-14 in living things depends on the level in the atmosphere. Carbon-14 is radioactive, and it decays exponentially over time. It takes about 5370 years for half of the carbon-14 to decay. By measuring the decay of carbon-14 in bones, it is possible to estimate the age of very old bones. At the Dallas Museum of Nature and Science, you will get to see a paleontology lab, and some interesting fossils.
Another bone measurement is Carbon-13, which is not radioactive. The amount of Carbon-13 depends on the diet, and the scientists in "Written in Bone" used Carbon-13 to find out about the diet of early Americans. Because corn was an important crop for Native Americans and colonists, and corn has a high level of Carbon-13 compared to other grains, the amount of Carbon-13 in the bones gives an indication of how long the person had lived in America. While a person living in England would have a typical Carbon-13 value in the range -21 to -18, a Native American would have a value in the range -15 to -9. For a colonist who was raised in England, then moved to North America, the Carbon-13 level would increase over time as they ate more corn. 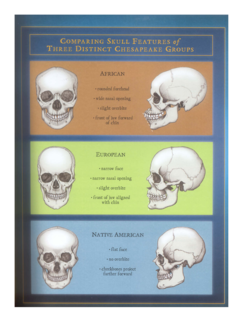
What else can we tell from studying bones? Certain diseases can give information about diet or age. Vitamin deficiency can cause rickets, softening of the bone. Osteoporosis is common in older women, and a spinal condition called DISH (diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis) is more common in older men. Eating certain foods or smoking a pipe can wear down teeth. Older people may have missing teeth. The age of younger people can be estimated based on the presence of baby teeth and molars.
The length of some bones allows us to predict the height of a person. These relationships were documented in the 1950s by Dr. Mildred Trotter, a professor of anatomy. This is useful to identify human remains from wars or airline disasters, for instance.
Use the equations below, or a chart, to estimate height from bone length:
Femur: 2.38 x l_femur + 61.41 cm = height in cm +/- 3.27
Humerus: 3.08 x l_humerus + 70.45 = height in cm +/- 4.05
Radius: 3.78 x l_radius + 79.01 = height in cm +/- 4.32

















What other people thought